When it comes to cardiac diagnostics, accuracy is non-negotiable. While most attention goes to the ECG machine or electrodes, one essential component often overlooked is the ECG leadwire. These cables play a vital role in transmitting accurate electrical signals from the body to the monitor—and if they’re compromised, so is the data.
Let’s take a closer look at how they work, what to consider when choosing them, and why it’s worth investing in the right ones.
What Are ECG Leadwires?
ECG leadwires are the cables that connect the electrodes attached to a patient’s skin to the electrocardiogram (ECG) machine. They help carry the electrical signals from the body’s surface to the monitor for analysis.
Without leadwires, there is no bridge between the patient and the monitoring system—and without that connection, no reliable readings.
Why Leadwire Quality Affects ECG Results
Even if your monitor and electrodes are top-notch, poor-quality leadwires can compromise signal clarity. Artifacts, electrical interference, and dropouts during monitoring are common when leadwires are damaged, low-grade, or incompatible.
The accuracy of the ECG trace depends just as much on the wire as it does on the software.
Types of ECG Leadwire Configurations
Leadwires vary based on how many leads they support. Common types include:
- 3-Lead ECG – Typically used for basic heart rate and rhythm monitoring.
- 5-Lead ECG – Common in telemetry and step-down units.
- 12-Lead ECG – Used for full cardiac diagnostics in emergency and cardiology settings.
Make sure your wire setup matches your patient monitoring needs.
Reusable vs. Disposable ECG Leadwires
Both types serve specific roles in different healthcare environments:
- Reusable: Durable and long-lasting, ideal for use in general wards and outpatient clinics.
- Disposable: Designed for one-time use to reduce infection risks—perfect for critical care units or isolation wards.
Many hospitals now use a mix depending on department protocols.
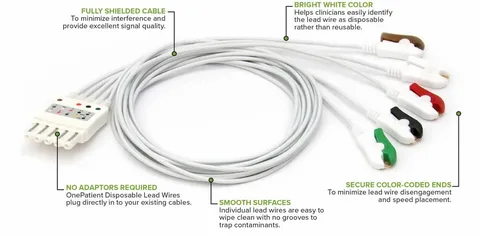
Features to Look for in a Reliable Leadwire
Not all ECG cables are equal. Before purchasing, check if your leadwires offer:
- Shielding for noise reduction
- Compatibility with your monitor brand
- Soft, flexible cable material
- Color-coded or labeled connectors
- Latex-free construction for safety
If you’re constantly troubleshooting ECG traces, your leadwires might be the hidden culprit.
Maintenance and Storage Tips
Even the best cables won’t last if they’re neglected. Keep your ECG leadwires in good shape with these simple practices:
- Clean after each use with a non-corrosive solution
- Store loosely coiled to prevent kinks
- Regularly inspect connectors for cracks or corrosion
- Replace worn or discolored wires immediately
This helps reduce the chance of errors or dropped signals during patient monitoring.
Compatibility: Don’t Skip This Step
Different monitors have different connector requirements. Always confirm that your ECG leadwires are compatible with your brand of monitor—whether it’s GE, Philips, Mindray, Nihon Kohden, or another model.
Mismatched connectors are one of the most common reasons for signal failure.
Where to Buy ECG Leadwires Online
If you’re looking for high-quality, clinically approved ecg leadwires that work seamlessly across major monitor systems, The Biomed Guys offers an excellent selection. Their catalog includes both reusable and disposable options, available in multiple configurations to suit your facility’s needs.
Their products are trusted by hospitals, urgent care centers, and biomedical professionals across the U.S.
Final Thoughts
Your ECG system is only as strong as its weakest link—and for many facilities, that link is the leadwire. A worn-out or low-quality cable can lead to flawed readings, misdiagnosis, and even patient harm.
By choosing reliable ecg leadwires, maintaining them properly, and ensuring compatibility, you’re not just following protocol—you’re supporting better care.